Sihlwald
Biodiversity Patterns in a Natural Forest Reserve: Effect of Habitat Amount and Distribution on Saproxylic Species
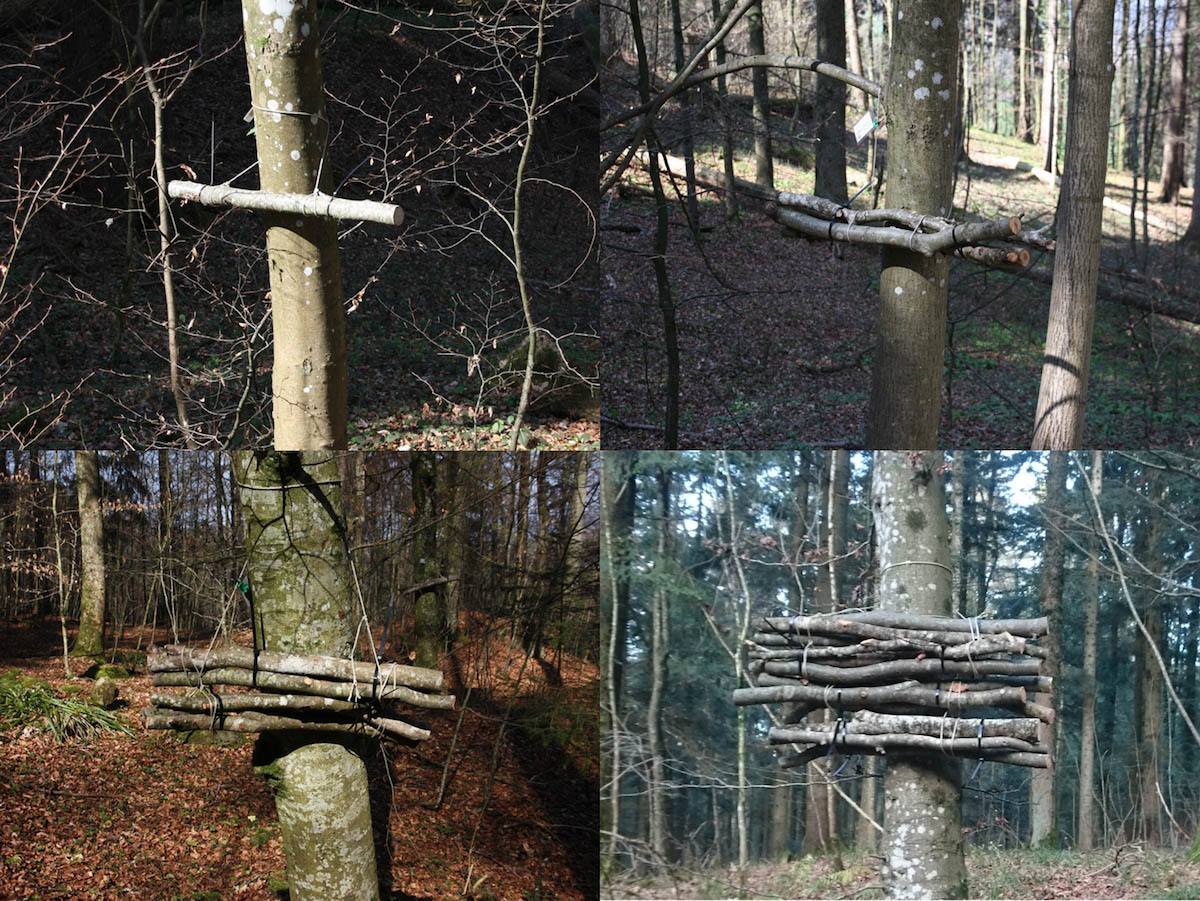
To understand biodiversity patterns and to improve conservation measures, detailed knowledge of the influencing environmental factors is needed. One of the most important factors is the availability of specific habitats. In forest ecosystems dead wood plays a major role as habitat for hundreds of species that depend on it (=saproxylic species). This species community is often used as an ecological indicator for near natural forests because saproxylic species are sensitive to the amount and quality of dead wood and other old growth structures.
Considering this, the communities of saproxylic beetles, wood inhabiting fungi, mosses and lichens are investigated in this study in the Zurich Wilderness Park Sihlwald. The goal is to understand how different species groups interact with their habitat and how habitat availability in terms of quantity and distribution influences biodiversity. To answer these questions the project includes a monitoring and an experimental approach.
The project is a collaboration between the Office of Landscape, Agriculture and Environment of the Canton of Zurich (division forest), the Zurich Wilderness Park Sihlwald, the Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research (WSL), the ETH Zurich and the School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL).