Former projects
Agrometric

In collaboration with AXA Climate, we hope to provide a simple, quick, and cost-effective, way to quantify biodiversity at the farm scale so that farmers may be further encouraged to make these changes by offering protection through agricultural insurance in the face of any potential loss to profits. Learn more
Andean Mountain Building - Bridging the gap between plate tectonics, landscape evolution, and biodiversity
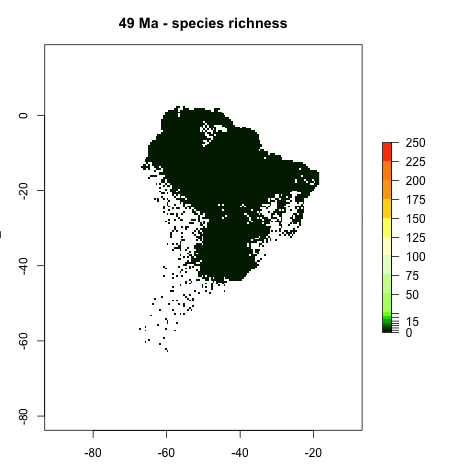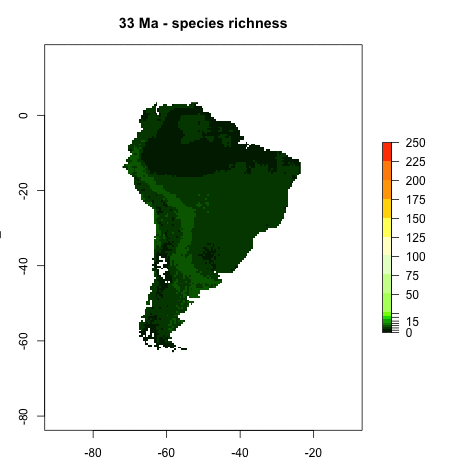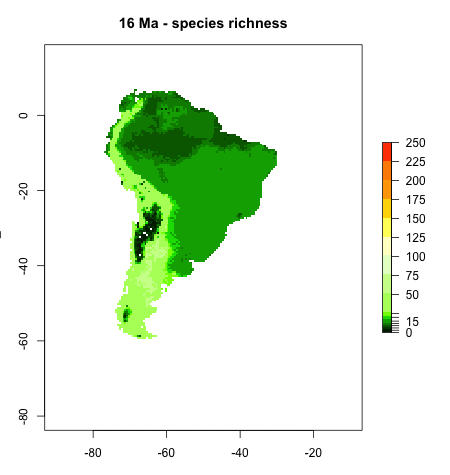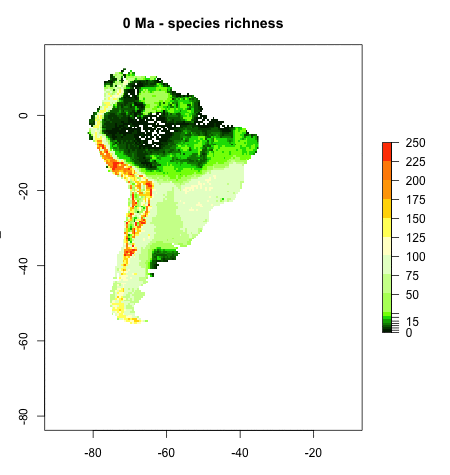
On geological timescales, plate tectonic and mountain building processes play a major role in shaping landscapes, especially in regions of high tectonic activity such as plate boundary zones. This project focusses on the tectonic and landscape evolution of South America, and studies how changes in landscape through geological time shaped modern biodiversity patterns. Learn more
Biodiversity, Earth, Climate Coupling in Yunnan (BECCY)

The Hengduan mountains (HDM), as a temperate biodiversity hotspot, hosts a huge amount of diversity, being one of the main “outliers” out of tropics. The complex geological and climate histories have shaping this mountain across milionaire scale while little is known about how these processes shaping diversity due to discipline gaps and lacking of high resolution data. The Biodiversity, Earth, Climate Coupling in Yunnan (BECCY) project is an interdisciplinary project, investigating the geolocal and climate processes in driving biodiversity patterns of plant and fishes in the Hengduan Mountains. Learn more
Biogeodynamics
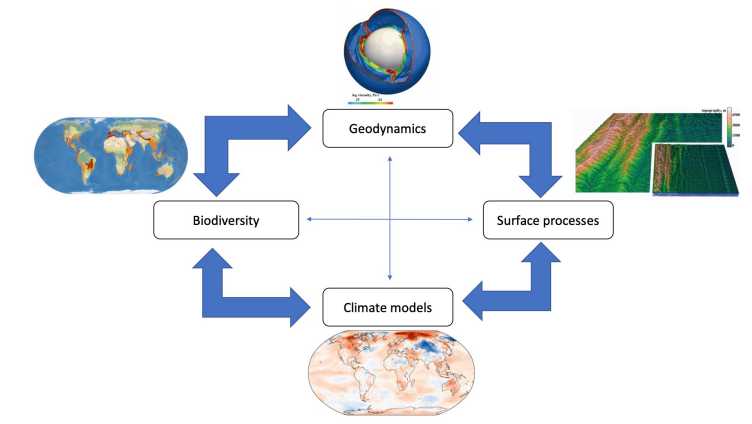
The biogeodynamics project aims to understand the complex co-evolution of Earth’s biosphere, climate and topography since the emergence of life by coupling models of the respective domains. Learn more
Broadening the scope of future visions for nature positive future

The project builds upon a participatory approach already applied for the creation of normative, nature-positive scenarios for future landscape development in Switzerland and expand this to the country of Peru. The scenarios constructed for Peru will be operationalized through simulation modelling exploring their impacts on land use change, biodiversity and the provision of ecosystem services within the agriculture and forestry domains. These impacts will be summarized qualitatively in terms of their effect on economic sectors of interest for policy makers and communities. Learn more
Calanda - Large-Scale Transplant Experiments
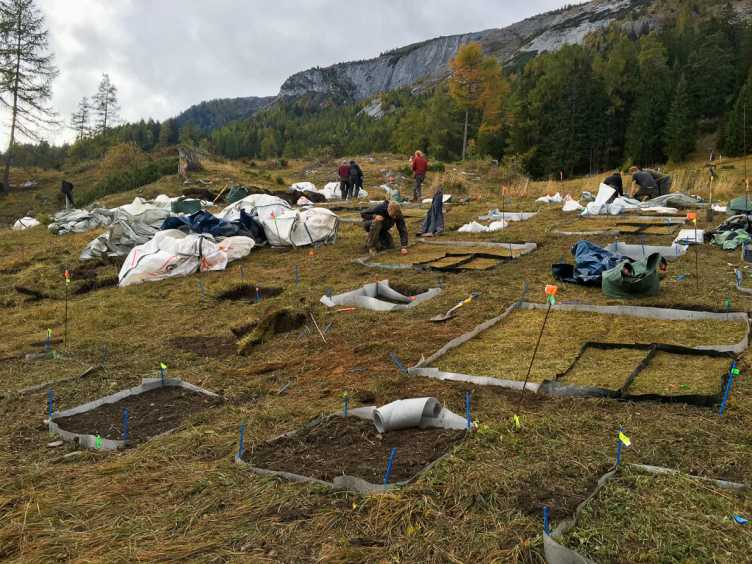

The Calanda project combines large-scale field experiments of alpine plant communities with mathematical models of dispersal and species-based and trait based interactions. To test how warming changes interactions between plant species and how fast these changes affect the community structure, alpine meadow communities will be transplanted to warmer sites downslope. Learn more
Chamois - The Determinants of the Population Genetic Structure of R. rupicapra in the Alps
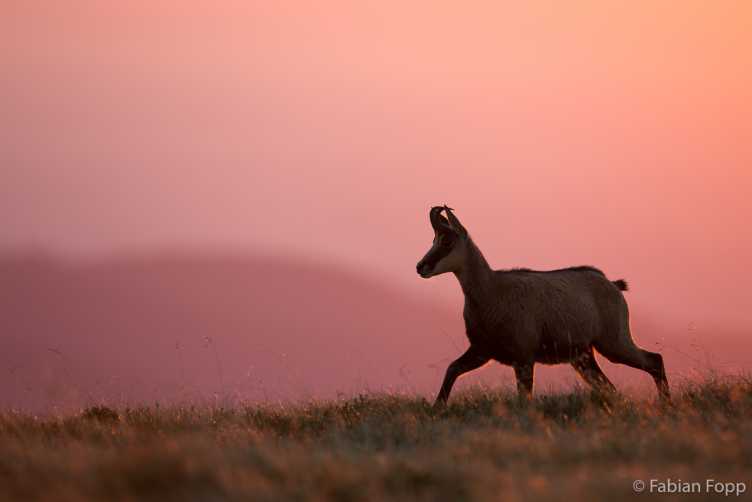

We combined habitat suitability models with process-based models and compared them to an extensive genomic data set of 449 ddRADseq chamois across the Alps to investigate the historical and contemporary factors shaping the population genetic structure. Learn more
Community Models - Modelling the Species Pool Effect in Grasslands Response to Climate Extremes
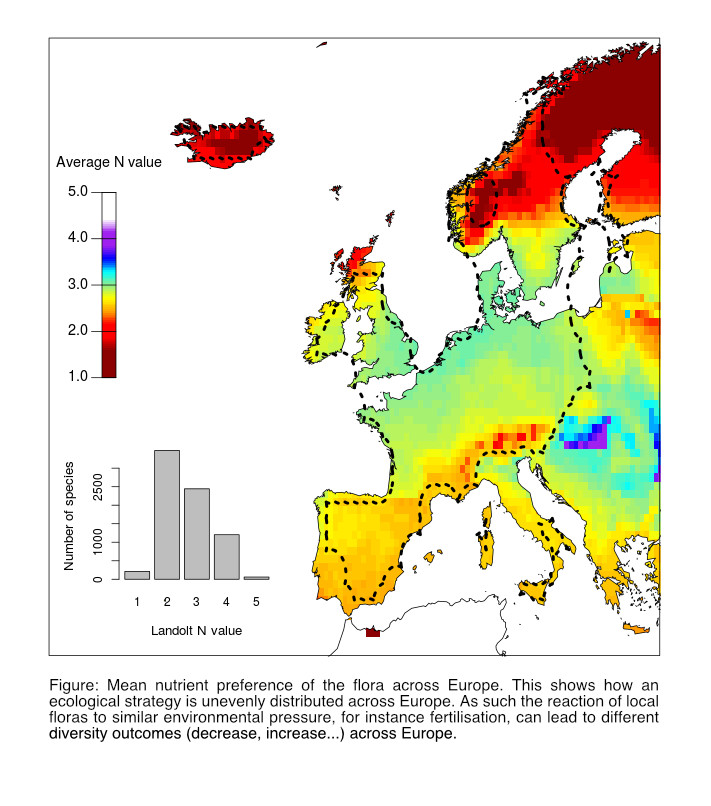
Realistic biodiversity forecasting is important for developing conservation initatives. Currently correlative models are used to predict species assemblages along environmental gradients. These models are suitable to predict regional pools but are more limited to forecast community assembly. This project develops simple mechanistic models to improve the prediction of local community structure. Learn more
ClimHerb - Response of Alpine Plant Communities to Biotic and Abiotic Changes
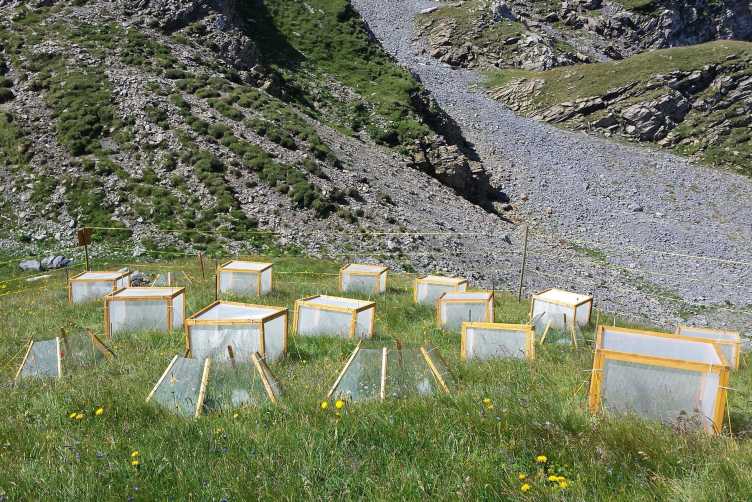

Many herbivores are shifting their distribution poleward and to higher elevation in response to climate changes. This may lead to new interactions between herbivore and plant species that have never co-occured. The ClimHerb project investigates how alpine plant communities respond to increased herbivory pressure and changes in biotic and abiotic conditions. Learn more
FuncNet - Land-Use Effects on Functional Networks and Consequences for Ecosystem Processes
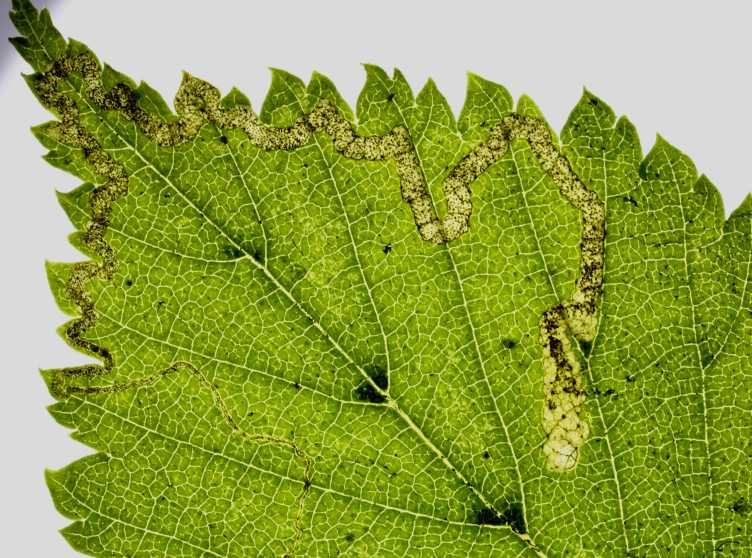

This projects aims to identify important insect traits responding to different filters such as historic and current landscape composition and local land use intensity and relate insect community composition to plant community composition using interactive networks and a trophic response-effect framework. A major focus is placed on insect herbivory, an important ecosystem process at the base of many food webs. Learn more
GEN3SIS - A Processed based Simulation Model

Biodiversity modelling is largely focused on contemporary ecological constrains on species diversity, while modelling the processes of diversification itself in a spatial context remains challenging. Dynamic simulation models may provide a better understanding of the way historical processes have shaped the distribution of biodiversity. For that, we are developing GEN3SIS (formely named GaSM), which is a processed based simulation model and infers biodiversity patterns from historical range dynamics taking into account eco-evolutionary feedbacks. Learn more
Global Drivers of Mountain Plant Diversity
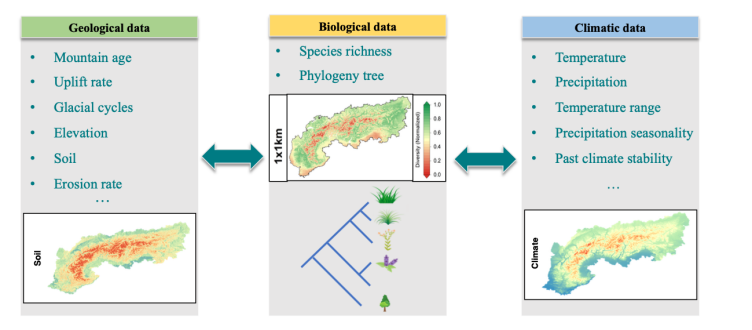
Mountains exhibit disproportionately high biodiversity of terrestrial organisms, which has long fascinated natural scientists and generated questions regarding the underlying processes. My project is aimed to provide a holistic view that explicitly incorporates geological, climatic, and biological processes at a fine spatial resolution, to understand the processes that have shaped contemporary patterns of plant biodiversity across global mountain systems through time. Learn more
Golden Eagle - Dispersal Ecology of Alpine Golden Eagles
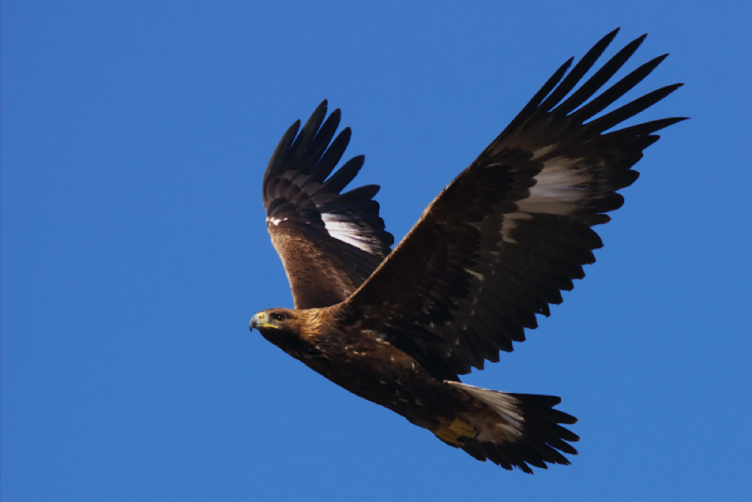

Natal dispersal is a key factor shaping population structure and dynamics. An individual is exposed to different biotic and abiotic conditions and has to weigh costs and benefits of different movement modes and behaviours while dispersing. We aim to study this important life history stage of Alpine golden eagles (Aquila chrysaetos) by equipping juveniles with high resolution GPS and accelerometer tags. Learn more
Insect Pests - Spatial Modelling of Insect Pests under Climate Change

Climate change is expected to affect the proliferation and spread of pests and pathogens since the abundance and generation time of insects depend primarily on ambient temperature. This project investigates the possible impact of harmful invasive insect pests on Swiss agriculture under future climate change scenarios. Learn more
Lif3web - Plant-Insect Interaction Networks

The Lif3web project investigates the ecological mechanisms shaping interactions between plants and insect herbivores along elevation gradients in the Alps. A better understanding of the structure of plant-insect interaction networks is important for a more realistic forecast of community responses to global changes. Learn more
Malefix - Machine Learning aided ForecastIng of related eXtremes
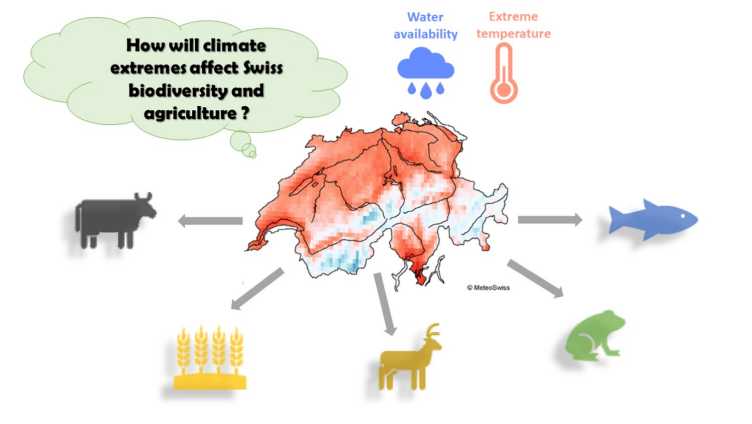
In this project, we will collect and compile data about physiological constraints of different species from the literature to predict the risk of Swiss biodiversity from sub-seasonal forecasts of extreme weather events. Extremes in water availability and air temperature will be investigated depending on the characteristics of the species. We will use a physiological modeling approach to assess the impact of extreme temperatures on species fitness under climate change scenarios. Learn more
Megafauna - Identify Refugia for Marine Megafauna
The megafauna project uses environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding to idenitify important habitats and biodiversity hotspots for marine megafauna. This should ultimately help to establish important protected areas in order to better protect the depleted populations of several marine species. Learn more
Metaweb - Swiss Interaction Networks
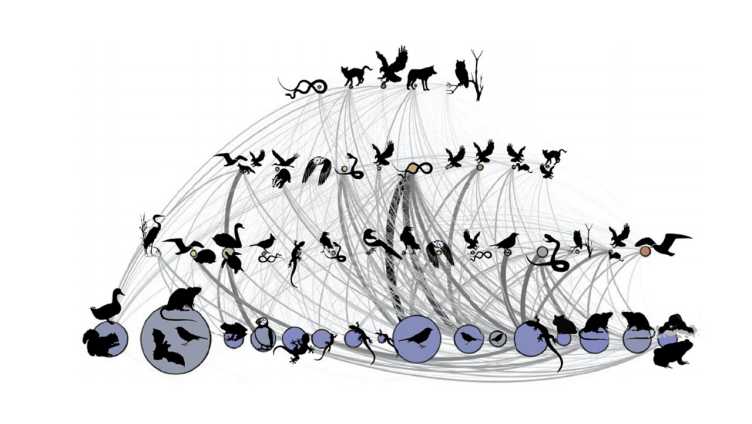
This project aims to generate a metaweb, a network of all possible interactions between species from a regional pool, with local interaction networks serving as distinct subsets of the regional metaweb. This allows to quantify the robustness of local networks to global changes to develop novel biodiversity change indicators to function alongside ongoing monitoring programmes. Learn more
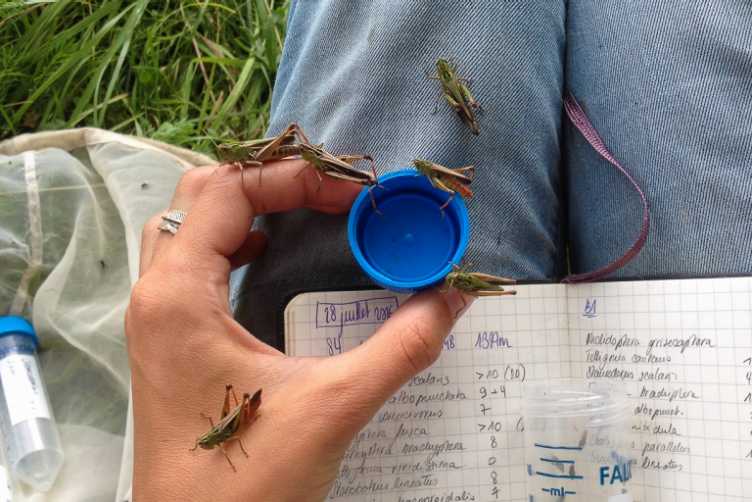
Orthosound - Using the Sound of Grasshoppers as Biodiversity Indicators
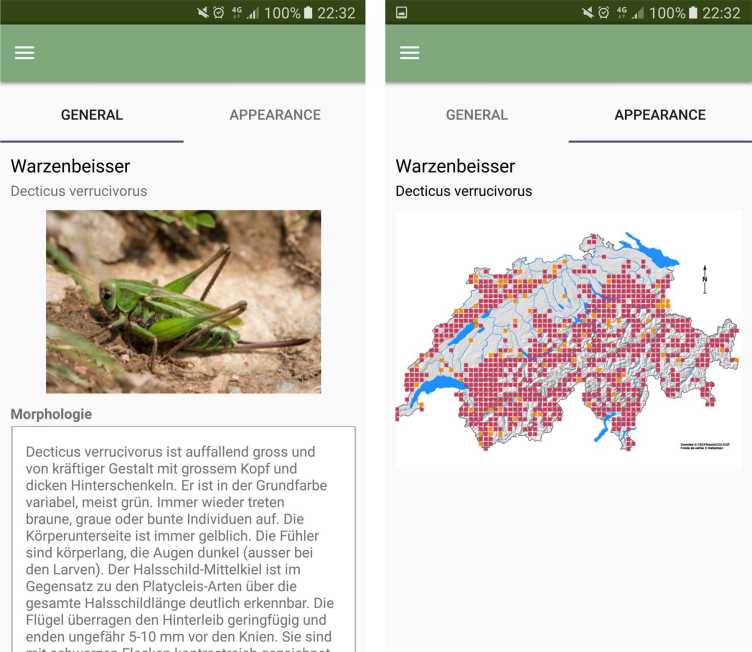
Soundscape ecology can be a powerful tool to monitor biodiversity. The goal of this project is to relate the sound properties of grasshoppers in grasslands to its biodiversity. Collecting biodiversity data is usually done by experts, which is both costly and only yields in limited amount of data. The development of a smartphone app allows to delegate the data collection to citizen to gather a larger amount of data. Learn more
Planetary Evolution
The planetary evolution project aims to reproduce the dynamic of living organisms in silico using a new generation of models that integrates spatially explicit dispersal with eco-evolutionary dynamics and speciation. Learn more
Processing of environmental DNA using artificial intelligence for ecosystem monitoring

In this project, we propose to harness a combination of machine learning approaches that transforms eDNA metabarcoding data into informative ecological indicators that improves ecosystem monitoring and decision making. As interpretation from eDNA signal is traditionally generated from the association of the DNA reads to taxonomic labels, we will first develop a machine learning method to associate sequences with a reference database and identify the taxonomic composition of eDNA in samples. Learn more
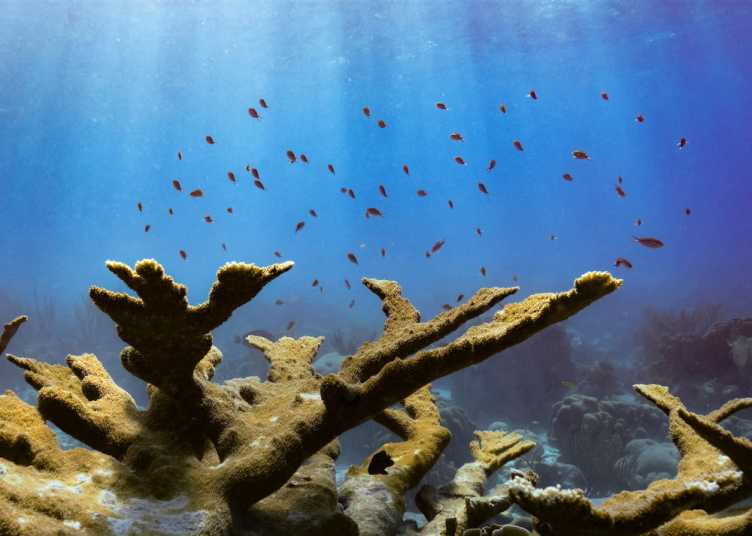
ReeFISH - Discovering Coral Reef Fish Biodiversity
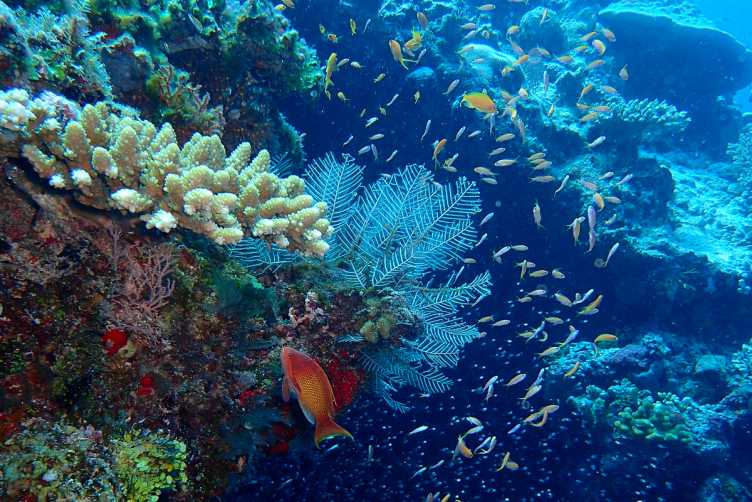

Through a combination of phylogenetic analyses, morphological measurements and population genetics, the ReeFISH project aims at understanding the ecological and evolutionary processes shaping fish biodiversity in coral reefs. Innovative methods will be used in this project, like an underwater stereo-camera system with extreme high quality to collect 3D morphological measurements of reef fishes. Learn more
Reef Futures - The future of reef services in the Anthropocene

Shallow-water reef ecosystems provide many services to coastal communities. The Reef Futures project aims to understand what environmental and socio-economic factors drives spatial variation in current day patterns of multiple ecosystem services provided by reef fishes. Furthermore, we will explore the dynamics of reef social-ecological systems in response to global environmental change, under different scenarios of climate, demographic and socio-economic futures. Learn more
Sihlwald - Biodiversity Patterns in a Natural Forest Reserve: Effect of Habitat Amount and Distribution on Saproxylic Species
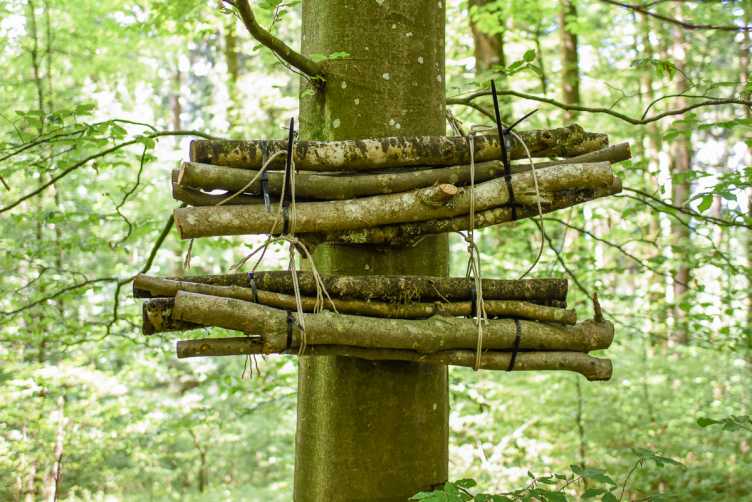

To better understand biodiversity patterns and improve conservation patterns, detailed knowledge of the influencing environmental factors, such as habitat availability, is needed. This project focusses on dead wood availability in forests and investigates how saproxylic species interact with their habitat and how habitat availability influences biodiversity. Learn more
Spatial and temporal dynamics of the Alpine Rock Ptarmigan in Switzerland
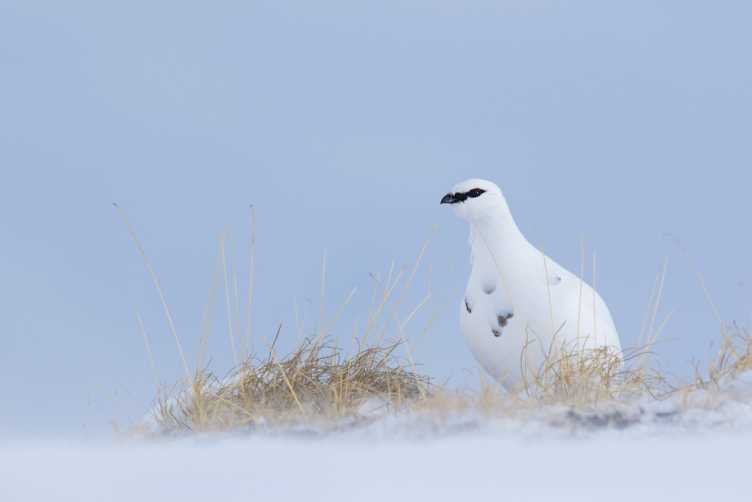

The population of the Alpine Rock Ptarmigan has strongly declined over the last decades in Switzerland. Using spatial models and different datasets of Ptarmigan recordings, this project aims to identify environmental factors associated with population dynamics in this species. Learn more
Summarizing ecology from simple to complex organisms
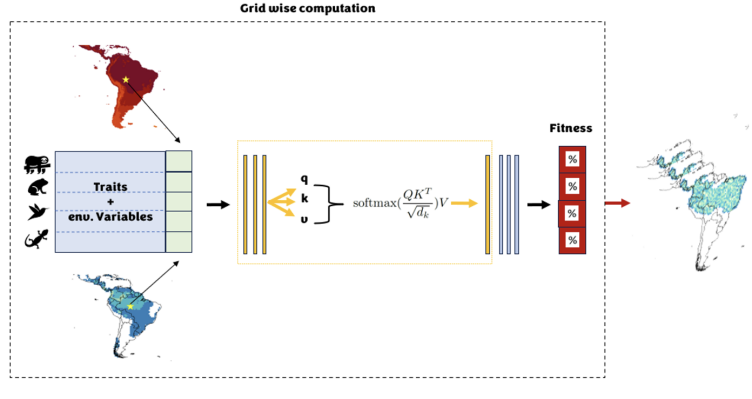
The project aims to use deep learning to model the ecological suitability of animal species by analyzing their morphological, ecological, and life-history traits, alongside climate data, to predict species distribution and interactions within ecosystems.The population of the Alpine Rock
Learn more
Swiss Catchment - The Correspondence of Biodiversity Gradients in Blue and Green Ecosystems

The goal of this project is to investigate biodiversity on the basis of 1200 catchments and sub-catchments in Switzerland. We will consider multiple taxonomic groups in terrestrial and freshwater ecosystems, and relying on mostly existing data from biodiversity monitoring, better understand the drivers of biodiversity in green and blue systems as well as their historical changes that have affected Swiss ecosystems.
Learn more
X-Prize - Remote Biodiversity Assessments

Although rainforests are the most diverse ecosystem, the knowledge of the species living in these iconic environemnts is still very limited. The XPrize Rainforest competition was designed to shed light into the rainforests of our planets which harbour many unidentified animals, plants and various chemical compounds that can potentially be used as drugs against human diseases. Learn more
Zackenberg - Effect of Climate Change on Arctic Vegetation

Climate change can shuffle terrestrial plant communities and therefore affect the structure and functioning of ecosystems. Studying both the distribution of arctic plant species and communities, as well as its drivers is necessary to predict changes in community composition in the future. Learn more
Monitoring ecosystem restoration with eDNA

In this project, we apply methods based on environmental DNA (eDNA) to advance terrestrial biodiversity monitoring, with a special focus on restored ecosystems. By measuring biodiversity change in forests at different stages of growth in Colombia, we aim to evaluate the application of eDNA based approaches in monitoring forest ecosystem recovery. Learn more