Robot-based automated collection of eDNA
Innovation of the design, perception and operation of drones to advance applications of eDNA technologies for biodiversity monitoring. Specifically focusing on the collection of eDNA from rainforest and general forest canopies.
The historic Kunming-Montreal Agreement of 18 December 2022 marked a significant milestone as over 200 countries came together to commit to the cessation and reversal of biodiversity loss. However, achieving a nature-positive future remains a formidable task, hindered in part by the absence of efficient and accurate tools for capturing comprehensive snapshots of global biodiversity. This is precisely where the integration of robots and environmental DNA (eDNA) technologies can truly make a difference.
The assessment of biodiversity through eDNA entails the collection and sequencing of genetic traces shed by local species within their environment. This innovative approach has revolutionized biodiversity monitoring by offering a non-invasive means to detect multiple species, including those that are notoriously elusive, from a single environmental sample. While eDNA surveys hold immense potential, the collection of samples continues to be a labor-intensive and costly aspect of the workflow. Robots equipped with specialized collectors and advanced perception capabilities have the power to automate and scale the process of eDNA collection. This can provide standardized and cost-effective biodiversity surveys even in challenging and inaccessible environments. By leveraging these automated systems, we can overcome the limitations of manual sampling, reduce cost, and expedite data acquisition.
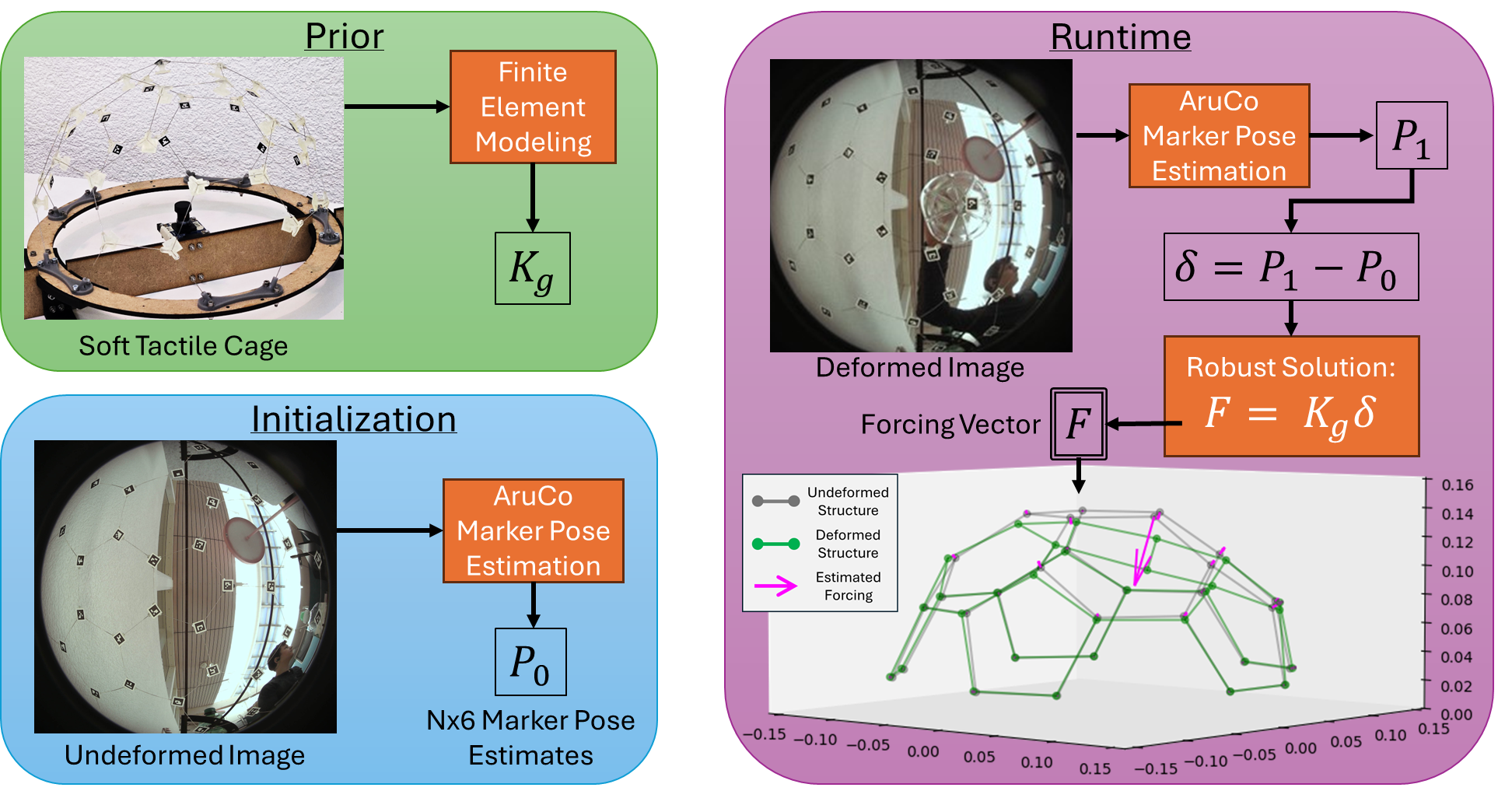
Forests are biodiversity hotspots and their canopies host the largest species richness within them, however they are difficult to access with conventional methods. At ETH we are designing an aerial caged robot with embodied tactile sensing to fly within dense rainforest canopy. This allows for repeatable and scalable swabbing of surfaces that would otherwise be prohibitively expensive to sample, and generalizes to any forest biome. Traditional remote sensors such as camera, lidar, IR, etc. would be blinded by the dense foliage in rainforest canopies. Further, the structurally heterogeneous and non-deterministic nature of physical contact wthin the canopy invalidate most aerial physical navigation approaches. Therefore, we are developing a novel tactile sensing and navigation approach that leverages the rotor cage as a sensing element.
Inquire with Ilya if interested in completing a Bachelor's or Master's thesis, or semester project, within this effort.

This project is supported by Hexagon Group.