Biodiversity history
Reconstructing geological and climate changes effects on historical biodiversity dynamics
SedaDNA studies have the potential to revolution the study of ecosystem changes and relate ecological processes to organism abundance changes over time. The method overcomes the limitation of taxonomic resolution of pollen and scarcity of macrofossils allowing more precise composition information for plants, but also allows for extracting information on animals. SedaDNA can be extracted from lake sediment cores at different depth of the core and the sediment can be used for DNA extraction followed by amplify DNA fragments of interest using PCR methods (metabarcoding) before sequencing.
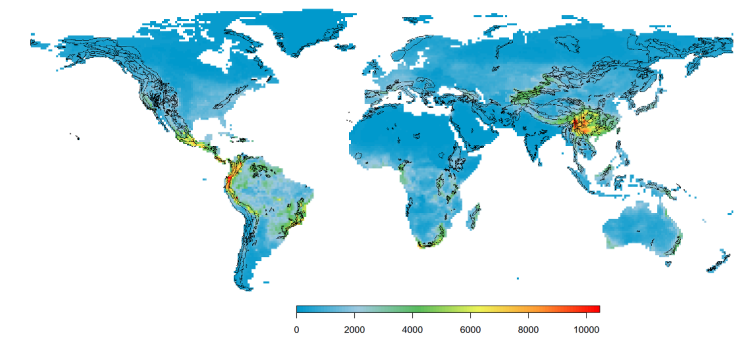
Bursting speciation from Geological DyNamics in mountains (BurGeoN)
Biodiversity state of an area is the result of a complex collective interplay of biological processes modulated by tectonic, climatic, and geomorphic changes of landscapes. Confined mountain areas exhibit remarkably high diversity with many young endemic and rare species suggesting that those systems that are not at equilibrium and speciation is still actively ongoing. We propose that lineages emerge over fast geological time scales and within narrow geographic zones because of locally active tectono-geomorphic processes, which increase speciation rate